Photographic Film
Definitions
Film Roll
A strip of film is made out of multiple layers.
- Supercoat: Protective Layer.
- UV Absorbing Layer: Aborbs the UV light so it does not appear on the emulsion layers.
- Emulsion Layers: Gelatin layers that contains silver halides that are sensitive to light.
- Subbing Layer: Adhesive layer between the film base and the emulsion layer.
- Film Base: The structurally supporting layer usually made out of plastic.
- Antihalation Backing: A dark layer that prevents light from bouncing back into the emulsion layer.
Silver Halide
An ionic compound 1 that forms between silver (positively charged) and a halogen (negatively charged).
Common halogens include
- Chlorine
- Bromine
- Iodine
- Fluorine
Which create the following ionic compounds with silver
- Silver \(Ag^+\) Chloride \(Cl^-\)
- Silver \(Ag^+\) Bromide \(Br^-\)
- Silver \(Ag^+\) Iodide \(I^-\)
- Silver \(Ag^+\) Fluoride \(F^-\)
When the silver halide is exposed to light, the energy from the photon is absorbed by the halide ions which excite the electrons to a higher energy state.
The electron in the halide ion then becomes mobile and is transfered to the silver ion to create metallic silver atoms.
These silver atoms are too small to see and creates an invisible image called the latent image that can then later be developed to become visible.
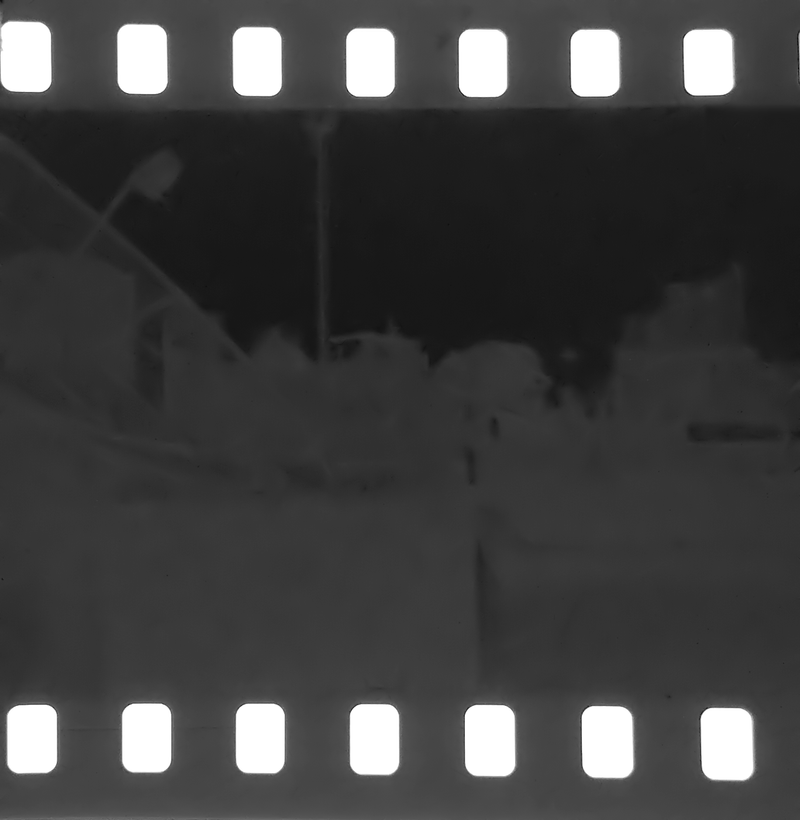

Development Process
The chemical process of treating the photographic film after they have been exposed to light to create a negative image.
-
Development: Alkaline chemical applied that reacts to the silver halide to chemically amplify the metallic silver clusters.
-
Stop Bath: Acidic solution used to neutralise the developer which halts the developer’s action.
-
Fixing: Thiosulfate salt solution used that removes the remaning unexposed silver halide, preventing the film from reacting to light any further.
Colour Film
The emulsion layer contain colour couplers that are dispersed around the silver halide crystals. They form coloured dyes during the development process.
The complementary colours are used in each layer to act as both a colour filter and the dye.
- Yellow dye forming coupler is located in the blue sensitive emulsion layer
- Absorbs as much blue light as possible and allows green and red to pass through
- Magenta dye forming coupler is located in the green sensitive layer
- Absorbs as much green light as possible and allows the red to pass through
- Cyan dye forming coupler is locatd in the red sensitive layer
The layers are ordered in this way for light absorption optimisation. The shorter wavelengths (blue) have a lower penetration power compared to the higher wavelengths (red)

Footnote
-
Chemical compound that is formed by electrostatic attraction between opppositely charged ions ↩